Blue System
-
- U.S. Navy's AGOR 27: R/V Neil Armstrong Maritime Reporter, May 2014 #40
On March 29, the Ocean Class Auxiliary General Oceanographic Research (AGOR) vessel hull number 27 started its official life as the R/V Neil Armstrong, the first research vessel named after a space explorer. Carol Armstrong, the widow of the famed astronaut, performed the christening duties during a brief sunbreak on a windy and rainy Pacific Northwest afternoon.
The number of illustrious speakers highlighted the rich diversity of agencies involved in the design, construction and operation of the vessel. Dick Nelson, President of Dakota Creek Industries (DCI), the construction shipyard, spoke first followed by Chris Chuhran, VP of Guido Perla and Associates, Inc. (GPA), the Seattle-based Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering firm that partnered with DCI for the design and build project. Chuhran said even though the keel was laid in June of 2012, the entire process had actually taken several years from its earliest idea phase to today’s ceremony. The final detail design evolved over many months with frequent reviews by NAVSEA, the Office of Naval Research (ONR), the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the University National Oceanographic Laboratory System (UNOLS). On several occasions, DCI hosted review meetings attended by more than 40 people.
Rear Admiral Jonathan White, USN, said the R/V Neil Armstrong would help the Navy and the United States “…know the ocean better than anyone else,” much like Armstrong’s trip to the moon helped us know the lunar world.
Chief of Naval Research, Rear Admiral Mathew Klunder, declared it a “magnificent vessel” that was “made and designed for the future.”
Dr. Susan Avery, President and Director of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) assured Mrs. Armstrong that her “husband’s legacy lives on in his namesake ship.” She described the ship as a “high-tech marvel” that is expected to perform its 40-year mission with distinction. The R/V Neil Armstrong will replace the R/V Knorr, in service since 1968, one year before Armstrong’s walk on the moon. The R/V Knorr, AGOR-15, is retiring after logging over one million miles in service to the Navy and WHOI.
Guests at DCI’s Transit Shed ceremony had only a short time to admire the sleek lines of the ship before tugs, taking advantage of the high tide, moved her back to the shipyard for completion of the interior systems.
Commissioning and finish work should be completed by August, followed by sea trials, after which the ship will then spend an additional six months in the Puget Sound area training the crews and adjusting the equipment before she heads for her new home port at WHOI in Massachusetts.
Initial vessel construction for the two-ship, $145-million-dollar project is funded by NAVSEA who will retain ownership of the vessel. Scientists from WHOI and around the world will be the primary users conducting year-round research in the North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans. WHOI will contribute $350,000 a year for maintenance and operation of the vessel.
Dr. Avery praised the modern design and ample computer lab space available on the R/V Neil Armstrong allowing scientists to analyze collected data in real time. She explained that the National Science Foundation (NSF) handles the complicated process of coordinating and scheduling research time on the ship. Pre-vetted, endorsed and funded projects are scheduled based on multiple factors; minimizing transit time, maximizing science time, matching and timing schedules and the number of days needed onboard. “Scheduling ship time in an integrated, inter-disciplinary way is a big planning effort,” said Dr. Avery. Research will include mapping of the seafloor, launching of buoys, ROVs and other equipment, studying how currents affect acoustic signatures, microbial content of the northern waters, discovering how climate change and sea level rise are impacting the North Atlantic, and how the ocean in turn impacts climate changes. The focus will be on the entire eco-system. The physics, biology and chemistry of the high latitude oceans will fall within the Neil Armstrong’s mission area.
Design Team
GPA was hired by DCI to provide a Basic Design during the Phase I NAVSEA design competition. When the team’s design was awarded the build contract in October 2011, GPA’s engineers and Naval Architects went to work on the detail design and production engineering. GPA collaborated with Siemens Marine for the propulsion and automation systems. Siemens will be designing, engineering, and commissioning the diesel electric and automation system.
GPA and DCI have partnered on projects in the past ranging from a Navy Sea Jet, an Advanced Electric Ship Demonstrator, to fire boats, ferries, tugs and trawlers. Both companies have worked on multiple Navy projects independently as well.
Shipyard
Dakota Creek Industries (DCI), located in Anacortes, Washington since 1975, began construction on AGOR 27 in mid-2012. The Navy exercised its option for a second vessel in February, 2012, and the shipyard began shifting its workload around to fit the second vessel into the schedule. Hollie Anthonysz, DCI Program Manager of vessel construction, said the shipyard’s first experience as the sole source on a military ship was positive and they are looking forward to the launch of the second ship.
DCI is a Puget Sound shipbuilding and repair facility specializing in steel and aluminum vessels up to 450 feet and 275 tons. Located in the deep waters of the Guemes channel, it offers a protected harbor with easy access to Pacific waters. Its facility includes a Syncrolift ship lift and a drydock.
Design Specifications
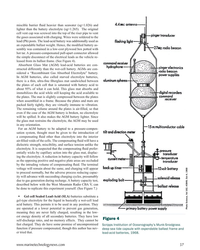
The vessels were designed for global operations in support of national security interests in the marine field, and other national oceanographic scientific endeavors. The ships are 238 ft in length overall, have a sustained speed of 12 kts, can stay at sea for a minimum of 40 days, and travel over 11,000 nautical miles without refueling.
In addition, they have the most modern scientific laboratory facilities and workshops afloat, high-tech computer and oceanographic equipment and hotel facilities to support 24 scientists and a crew of 20. They are built to ABS Under 90 Meter rules, and will be certified as A1, Circle E, AMS, ACCU, NIBS, Ice Class D0, and UWILD. The design is also compliant with 46CFR Subchapter U (Oceanographic Vessels).
Working deck space is a premium in oceanographic work. The AGOR vessels have 2,557 sq. ft. of clear deck space with 1,873 sq ft of that space on the open aft deck. Design specifications included being fully operational in Sea State 4 and able to handle dynamic positioning relative to a fixed position in Sea State 5 with a 35-knot wind and 2-knot current.
Additionally, the ship had to be as operationally quiet as possible. A great deal of ocean research involves listening. Excessive ship noise would negate that effort. GPA’s unique hull design meets the Bubble Sweepdown performance requirement of the original specifications by diverting bubbles away from the sensitive sonar area. Model tank tests performed in Poland confirmed the Phase 1 design efforts met the Navy’s exacting standards. Completing the noise dampening goal, designers chose systems, defined equipment locations and designed special installation methods with acoustics as a priority.
Equipment
DCI has teamed with a multitude of local, national and international vendors to outfit the ship with the best equipment available, meeting the various needs and requirements of the scientists for a quiet, efficient, fully integrated and highly resilient blue-water platform from which they can perform their experiments and studies.
Over the next two months, Siemens will be installing their new Blue system. This advanced, multi-drive, low-voltage system manages the speed of various AC propulsion motors controlling the propellers, stern thruster and bow thruster. The system provides enhanced reliability with multiple failsafe features, lower maintenance costs, increased efficiency, and increased operational ease for the crew. Reduced fuel consumption results in lower greenhouse gas emissions. Siemens is also supplying the majority of the electrical switchgear, the ACCU automation, and condition-based monitoring system.
The vessel uses four vibration-isolated Cummins QSK38-DM main generators providing a maximum of 3952 kW integrated electric power for all functions of the ship, including propulsion. The integrated diesel-electric plant allows for multiple generator configurations, ensuring the diesel engines operate at peak efficiency at all times.
A unique feature of the electric propulsion will be a “combinator” style control function integrating management of motor speed and propeller pitch on the Hundested-supplied Controllable Pitch Propellers.
Although fairly common in controllable pitch systems with direct drive diesels, use of the combinator control is unusual in variable-speed electric drive systems. The combinator increases operational flexibility by allowing the operator to set the propeller at its most efficient setting across a range of operations including heavy towing and cruising.
Design specifications were stringent for deck cranes and winches. They needed the capacity to load equipment weighing more than 20,000 pounds including the deployment of ROVs, buoys and other heavy equipment. The stern frame required a minimum of 12-foot inboard and outboard reach. As designed, the frame provides 15 feet of clearance above the deck and 27 feet of clear space between the block attachment points, all while maintaining a Dynamic Safe Working Load of 30,000 pounds through the full range of motion. Allied Marine supplied the stern frame along with the portable TK4-30 portable crane and the TK 70-70 aft-deck Main Crane. They also supplied the Motion Compensated CTD Handling System and the Starboard Side Handling Device, both of which extend to the waterline for improved safety and load control.
Seattle based Markey Machinery supplied two electric-motor driven CAST-6-125 Hydrographic Winches, and the DETW-9-11 Traction Winch, both with AC Variable Frequency Drives System and electric motors for precise control.
Kongsberg Maritime, a 200-year-old Norwegian company, produces a full line of specialty SONARS used in scientific research, fisheries and oil exploration. For Phase III of the project, Kongsberg will supply advanced SONAR systems. Although specifics are not confirmed at this time, projected equipment includes deep water and mid-water Multi-beam units, a HiPAP Gantry with a Sonardyne single beam survey system, and a SONAR Synchronization System. A Sub-bottom Profiler SONAR is expected as well. Additional equipment plans include a Transducer Array, a Mid-water Echo Sounder, and three Current Profilers operating at different frequencies, all are scheduled for installation in Phase III, subject to change as the project progresses.
AGOR 28, the second vessel in the Armstrong Class, will be named R/V Sally Ride in honor of the first female astronaut and the youngest person to go into space. The R/V Sally Ride will be operated by Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California, San Diego, where Ms. Ride was a faculty member before becoming an astronaut. The second vessel will mirror the basic ship equipment with some variations in the scientific outfitting. The christening date for the Sally Ride is scheduled for later this summer.
AGOR 27 Neil Armstrong Main Particulars
Yard Dakota Creek Industries (DCI),
Designer Guido Perla and Associates, Inc.
Owner NAVSEA
Operator WHOI
Organizations NAVSEA, the Office of Naval Research (ONR), the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the University National Oceanographic Laboratory System (UNOLS), Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI
Class ABS
Main engines Cummins
Cranes Allied Marine
Winches Markey Machinery
Sonar Kongsberg Maritime
Survey Sonardyne
Schat Harding Rescue Boat Davit SA135
Schottel Stern Thruster 1x 620kW (830 HP)
White Gill Bow Thrusters 1x 686kW (920 HP)
MTU Emergency Generator 1x 210kW (280 HP)
Propulsion System Siemens Marine
Over the next two months, Siemens will be installing their new Blue system. This advanced, multi-drive, low-voltage system manages the speed of various AC propulsion motors controlling the propellers, stern thruster and bow thruster. The system provides enhanced reliability with multiple failsafe features, lower maintenance costs, increased efficiency, and increased operational ease for the crew. Reduced fuel consumption results in lower greenhouse gas emissions. Siemens is also supplying the majority of the electrical switchgear, the ACCU automation, and condition-based monitoring system.
Markey
• 2x type CAST6-125 Deep Sea Research Winches with active motion compensation
• 1x type DETW-9-11 All-Electric Traction Winch System with two storage drums
• 1x instrumented flagging block
• 1x ship board wire monitoring system
• 1xtype WES-23 Electric Anchor Windlass with two wild cats and two warping heads.
Kongsberg
• Deep Water Multibeam Survey System EM-122
• Mid Water Multibeam Survey System EM-710
• Single Beam Survey System EA-600
Allied Systems
• Stern Frame A-30
• Main Crane TK70-70
• Portable Crane TK4-30
• CTD Handling System CTD-Lars
• Starboard Side Handling Device(As published in the May 2014 edition of Maritime Reporter & Engineering News - http://magazines.marinelink.com/Magazines/MaritimeReporter)
-
- Great Ships of 2014: R/V Neil Armstrong - Multifaceted Sea Explorer Maritime Reporter, Dec 2014 #50
designers chose systems, defined equipment locations, and designed special installation methods with acoustics as a priority. Siemens installed its new Blue system, an advanced, multi-drive, low-voltage system manages the speed of various AC propulsion motors controlling the propellers, stern thruster and bow
-
- AGOR 27 Comes to Life as the R/V Neil Armstrong Marine Technology, May 2014 #40
blue-water platform from which they can perform their experiments and studies. Over the next two months, Siemens will be installing their new Blue system. This advanced, multi-drive, low-voltage system manages the speed of various AC propulsion motors controlling the propellers, stern thruster and
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 4th Cover
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 4th CoverGlow a little longer. Superior sensor performance on a rmance on a – – RBRtridentfraction of the power RBRtridente teee ackscatter or turbidity with hi i in n n t t th h h he e e s sa a am m m me Measure chlorophyll a, fDOM, and backscatter or turbidity within the same e e sensor package using the
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 48
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .www.birns.com . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Please visit us online 19 . . . . .Blueprint Subsea . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .www.blueprintsubsea.com . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .+44 (0) 1539 531536 5 . . .
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 45
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 45ronments. The new agreement will address speci? c techni- cal gaps in the UUV defense and offshore energy markets especially for long duration, multi-payload mission opera- tions where communications are often denied or restricted. As part of the new alliance, Metron’s Resilient Mission Autonomy portfolio
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 44
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 44NEW TECH OCEANOLOGY INTERNATIONAL 2024 Image courtesy Metron/Cellula Teledyne Marine acquires Valeport: Matt Quartley, MD, Valeport and Ole Søe-Pedersen, VP & Image courtesy Teledyne Marine GM Teledyne Marine announce the deal in London. Pictured (L-R): Cellula Robotics, President, Eric Jackson, Metron
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 43
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 43Image courtesy Kongsberg Discovery Image courtesy Teledyne Marine New Products Teledyne Marine had its traditional mega-booth at Oi, busy start to ? nish. Image courtesy Greg Trauthwein offers quality sub-bottom pro? ling capability without the need tion of offshore windfarms. GeoPulse 2 introduces new
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 42
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 42NEW TECH OCEANOLOGY INTERNATIONAL 2024 Image courtesy Greg Trauthwein Image courtesy BIRNS MacArtney launches the new ultra-compact ø12.7 mm SubConn Nano connector. Innovative connectivity built on 45 years of ? eld-proven and market-trusted design. Image courtesy MacArtney Birns celebrated its 70th
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 41
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 41Image courtesy Outland Technology Image courtesy Exail Image courtesy Submaris and EvoLogics Vehicles The ROV-1500 from Outland Technology represents a leap forward in underwater robotics, a compact remotely operated vehicle (ROV) weighing in at less than 40 lbs (19kg) the ROV- 1500 is easy to transport
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 40
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 40NEW TECH OCEANOLOGY INTERNATIONAL 2024 All photos courtesy MTR unless otherwise noted NEW TECH, PARTNERSHIPS LAUNCH IN LONDON With Oceanology International now one month in the rear-view mirror, MTR takes a look at some of the interesting technologies launched before, during and after the London event.
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 39
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 39Photo courtesy Global Ocean Design Figure 7 A 35Ah AGM lead-acid battery is tested using the West Mountain Radio CBA to show the effect of simply ? lling the battery voids with mineral oil as a compensating ? uid. The CBA is programmed to cut-off at a voltage of 10.50v. The top line (red) shows the
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 38
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 38LANDER LAB #10 Photo courtesy West Mountain Radio Photo courtesy of Clarios/AutoBatteries.com Figure 6 The West Mountain Radio Computerized Battery Analyzer (CBA V) attaches to a Figure 5 laptop by a USB-B cable, and to a battery by Powerpole® Connectors. Exploded view of an AGM lead-acid battery.
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 37
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 37miscible barrier ? uid heavier than seawater (sg=1.026) and lighter than the battery electrolyte (sg=1.265). The original cell vent cap was screwed into the top of the riser pipe to vent the gases associated with charging. Wires were soldered to the lead (Pb) posts. The lead-acid battery was additionall
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 36
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 36LANDER LAB #10 Of special interest for marine applications, LiPo batteries are Shipping any kind of lithium battery can be a challenge, and offered in a “pouch” design, with a soft, ? at body. The pouch IATA regs vary with the batteries inside or outside an instru- is vacuum-sealed, with all voids ?
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 33
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 33regulated industry in the world.” How- ever, commercial success depends on many factors, not least a predictable OPEX. Over the past four years, SMD has worked with Oil States Industries to calculate cost per tonne ? gures for prospective customers. Patania II uses jet water pumps to Oil States’
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 32
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 32FEATURE SEABED MINING by a sea? oor plume from its pilot collection system test. pact, nodule collection system that utilizes mechanical and The Metals Company recently signed a binding MoU with hydraulic technology. Paci? c Metals Corporation of Japan for a feasibility study on The company’s SMD
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 31
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 31The Allseas-designed production system consists of the Hidden Gem production vessel at the surface, an airlift riser system and jumper hose, and the pilot nodule collector vehicle at the sea? oor. Image courtesy of Allseas www.marinetechnologynews.com 31 MTR #3 (18-33).indd 31 4/4/2024 2:12:41
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 30
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 30FEATURE SEABED MINING bilical. It has passive heave compensation which nulli? es the necott. “The focus since then has been on scaling while en- wave, current and vessel motions that in? uence loads in the suring the lightest environmental impact,” says The Metals power umbilical. The LARS can
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 29
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 29n January, Norway said “yes” to sea- bed mining, adding its weight to the momentum that is likely to override the calls for a moratorium by over 20 countries and companies such as I Google, BMW, Volvo and Samsung. Those against mining aim to protect the unique and largely unknown ecology of the sea?
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 25
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 25Auerbach explained that ideally, “one ? ed layers of geothermal activity,” noted changes over an area of 8,000 km2. They would have both instruments: seismom- Skett, “and the change in salinity and dis- found up to seven km3 of displaced ma- eters to detect and locate subsurface ac- solved particles for
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 19
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 19About the Author vey with the pipe tracker is not required, resulting in signi? - Svenn Magen Wigen is a Cathodic Protection and corrosion control cant cost savings, mainly related to vessel charter. expert having worked across The major advantage of using FiGS on any type of subsea engineering, design
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 18
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 18TECH FEATURE IMR There are also weaknesses in terms of accuracy because of FiGS Operations and Bene? ts signal noise and the ability to detect small ? eld gradients. In Conventional approaches to evaluating cathodic protection this process there is a risk that possible issues like coating (CP)
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 17
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 17• Integrity assessment, and otherwise covered, e.g., by rock dump. As for depletion of • Mitigation, intervention and repair. sacri? cial anodes, this can be dif? cult or even impossible to Selecting the best method for collecting the data these work- estimate due to poor visibility, the presence of
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 15
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 15sensor options for longer mission periods. About the Author For glider users working in ? sheries and conservation, Shea Quinn is the Product Line Manager the Sentinel can run several high-energy passive and active of the Slocum Glider at Teledyne Webb acoustic sensors, on-board processing, and imaging
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 11
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 11assist in identifying mines and act as a neutralization device. About the Author Bottom mines pose even greater chal- David R. Strachan is a defense analyst and founder of lenges. Unlike contact mines, bottom Strikepod Systems, a research and strategic advisory mines utilize a range of sensors to
-
 )
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 9
)
March 2024 - Marine Technology Reporter page: 9from marinas along the western coast. The exact number of lizing laser detection systems can detect mines just below the mines, as well as their locations, remains largely a mystery, surface, even those hiding in murky water. The Airborne Laser although reports suggest that over three hundred have been
