
Page 83: of Offshore Engineer Magazine (Apr/May 2013)
Read this page in Pdf, Flash or Html5 edition of Apr/May 2013 Offshore Engineer Magazine
West Africa Focus
NW Africa’s potential displayed off Morocco
The North African Atlantic Shelf is survey-wide, it has a core of complex stratigraphic succession.
T continues to be a region of intense thicker, blocky material that came In some of the earliest deposits, academic activity, and recently, to rest after passing over the distal- found just above the rifted base-
E&P companies such as Repsol and most edge of the Triassic-age salt ment rock, we see a series of
Chevron have renewed their inter- province, found along much of the Jurassic-age fans with high-ampli- est in the hydrocarbon potential Atlantic margin. tude seismic responses. Discrete of its deeply buried sediments. As Salt diapirs pepper the survey inner and outer fans form the deepwater-drilling technologies with shallow salt pillows, obstruct- boundaries of the complex, which have evolved and our understand- ing subsalt stratigraphy, actively is overlain by small distributary ing of lower-slope geology has subsiding minibasins, salt bridges channels. Larger canyons originate improved, the favorability of new between diapirs, and a distal, deep- updip and cross over the basement deepwater exploration targets has seated, toe-thrust salt body. This half-grabens. grown. Passive continental margins, toe-thrust diapir formed a paleo- Since only a few of these features particularly those in salt provinces, high during the Jurassic that led to were previously penetrated by well have proven to be some of the best adjacent, large, 120m-thick, fne- bores, new deepwater-exploration areas where structural geology, grained contourites, which were de- activities will not only lead to new stratigraphy, and salt tectonics can posited as bottom currents became drilling technologies and docu- combine to form intricate hydrocar- concentrated near the paleohigh. mented reserves for offshore NW bon traps with inherently compli- Furthermore, there is a well-imaged Africa, but also have the potential cated drilling strategies. paleo-volcano that had a positive to greatly expand our knowledge
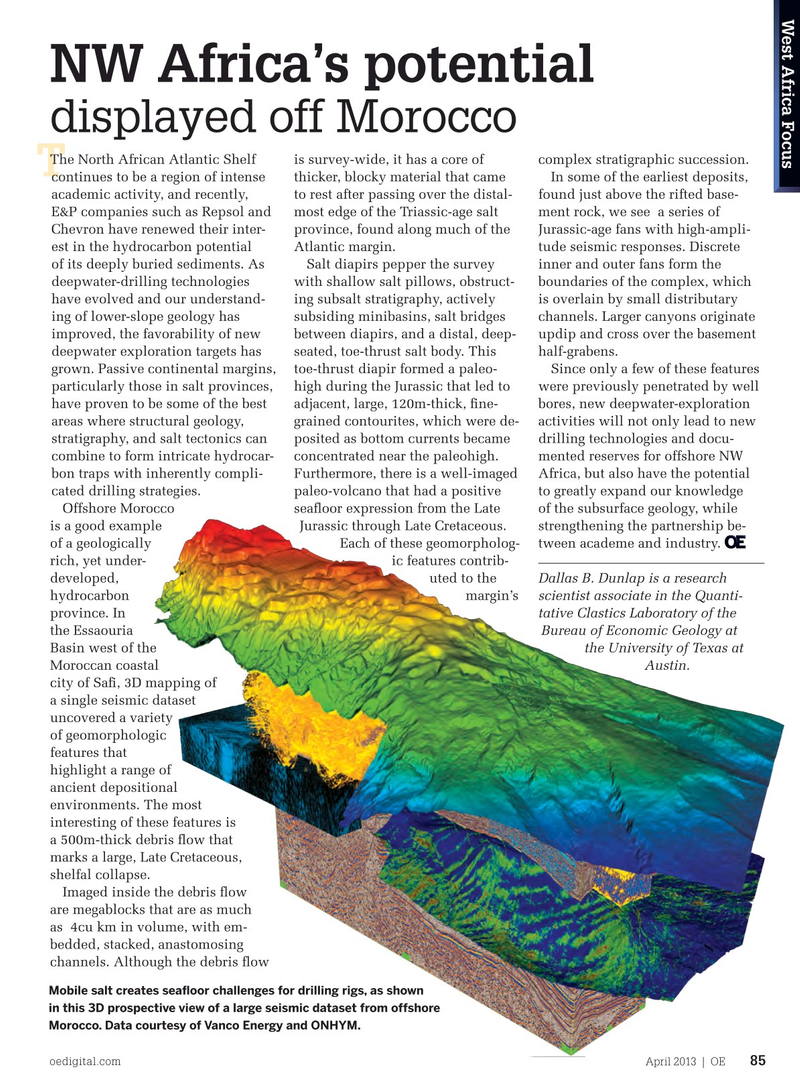
Offshore Morocco seafoor expression from the Late of the subsurface geology, while is a good example Jurassic through Late Cretaceous. strengthening the partnership be- of a geologically Each of these geomorpholog- tween academe and industry. rich, yet under- ic features contrib- developed, uted to the Dallas B. Dunlap is a research hydrocarbon margin’s scientist associate in the Quanti- province. In tative Clastics Laboratory of the the Essaouria Bureau of Economic Geology at
Basin west of the the University of Texas at
Moroccan coastal Austin.
city of Saf, 3D mapping of a single seismic dataset uncovered a variety of geomorphologic features that highlight a range of ancient depositional environments. The most interesting of these features is a 500m-thick debris fow that marks a large, Late Cretaceous, shelfal collapse.
Imaged inside the debris fow are megablocks that are as much as 4cu km in volume, with em- bedded, stacked, anastomosing channels. Although the debris fow
Mobile salt creates seafoor challenges for drilling rigs, as shown in this 3D prospective view of a large seismic dataset from offshore
Morocco. Data courtesy of Vanco Energy and ONHYM.
oedigital.com April 2013 | OE 85
Dunlap_Morocco_RHP.indd 85 4/1/13 1:40 AM

 82
82
 84
84