
Page 52: of Offshore Engineer Magazine (May/Jun 2024)
Read this page in Pdf, Flash or Html5 edition of May/Jun 2024 Offshore Engineer Magazine
GREEN HYDROGEN ELECTROLYZERS
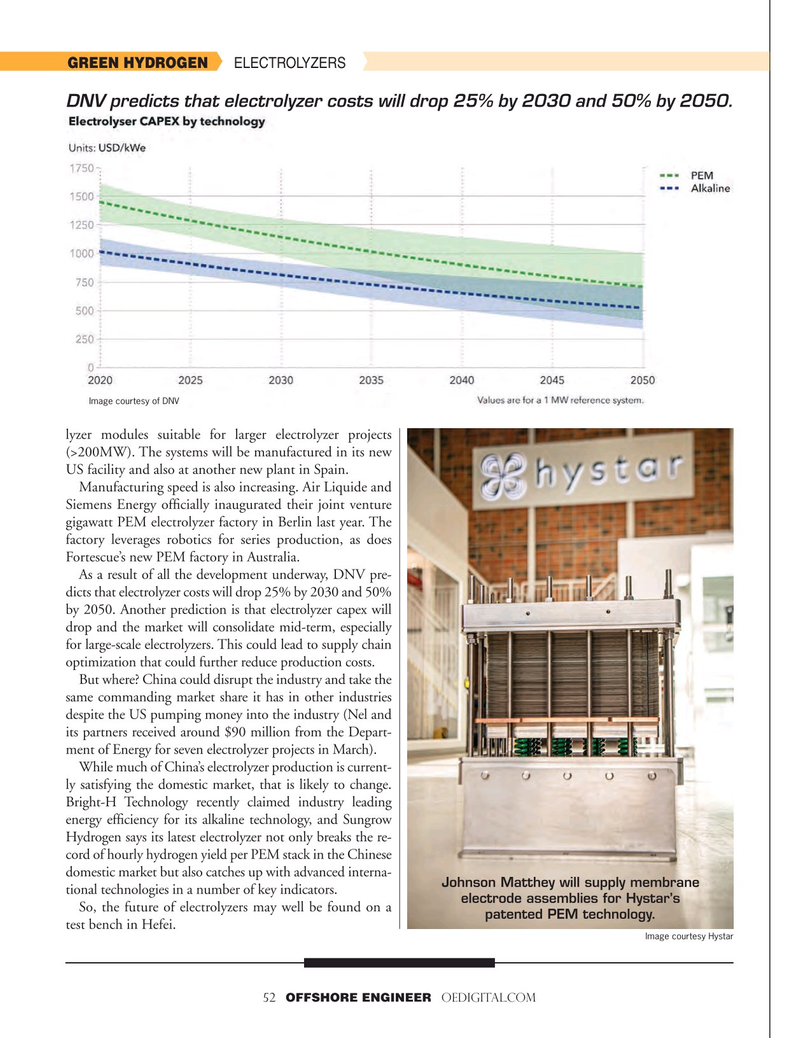
DNV predicts that electrolyzer costs will drop 25% by 2030 and 50% by 2050.
Image courtesy of DNV lyzer modules suitable for larger electrolyzer projects (>200MW). The systems will be manufactured in its new
US facility and also at another new plant in Spain.
Manufacturing speed is also increasing. Air Liquide and
Siemens Energy offcially inaugurated their joint venture gigawatt PEM electrolyzer factory in Berlin last year. The factory leverages robotics for series production, as does
Fortescue’s new PEM factory in Australia.
As a result of all the development underway, DNV pre- dicts that electrolyzer costs will drop 25% by 2030 and 50% by 2050. Another prediction is that electrolyzer capex will drop and the market will consolidate mid-term, especially for large-scale electrolyzers. This could lead to supply chain optimization that could further reduce production costs.
But where? China could disrupt the industry and take the same commanding market share it has in other industries despite the US pumping money into the industry (Nel and its partners received around $90 million from the Depart- ment of Energy for seven electrolyzer projects in March).
While much of China’s electrolyzer production is current- ly satisfying the domestic market, that is likely to change.
Bright-H Technology recently claimed industry leading energy effciency for its alkaline technology, and Sungrow
Hydrogen says its latest electrolyzer not only breaks the re- cord of hourly hydrogen yield per PEM stack in the Chinese domestic market but also catches up with advanced interna-
Johnson Matthey will supply membrane tional technologies in a number of key indicators.
electrode assemblies for Hystar’s
So, the future of electrolyzers may well be found on a patented PEM technology.
test bench in Hefei.
Image courtesy Hystar 52 OFFSHORE ENGINEER OEDIGITAL.COM

 51
51
 53
53