
Page 8: of Maritime Reporter Magazine (May 2, 2010)
Read this page in Pdf, Flash or Html5 edition of May 2, 2010 Maritime Reporter Magazine
FEATURE SHIP ISHIN-III
Mitsui O.S.K. Lines has completed the concept for its third in a series of next-generation vessels, which will be technically practical in the future. The latest concept is for an environment- friendly, large-scale iron ore carrier called the ISHIN-III that is designed to play a key role in future resource transport. MOL already operates the very large iron ore carrier Brasil Maru that offers a high level of environmental performance thanks to its pioneering transport concept and technologies. Delivered in De- cember 2007, the 320,000-DWT Brasil Maru, which measures 1115 x 197 ft. (340 x 60 m) with a main engine output of 23,000 kW, is one of the world’s largest iron ore carriers.
Because it will be another several years before ISHIN ves- sels become technically feasible to build, the company could not give specific cost figures as there are no current plans to construct an ISHIN vessel, according to Yoshikazu Kawagoe,
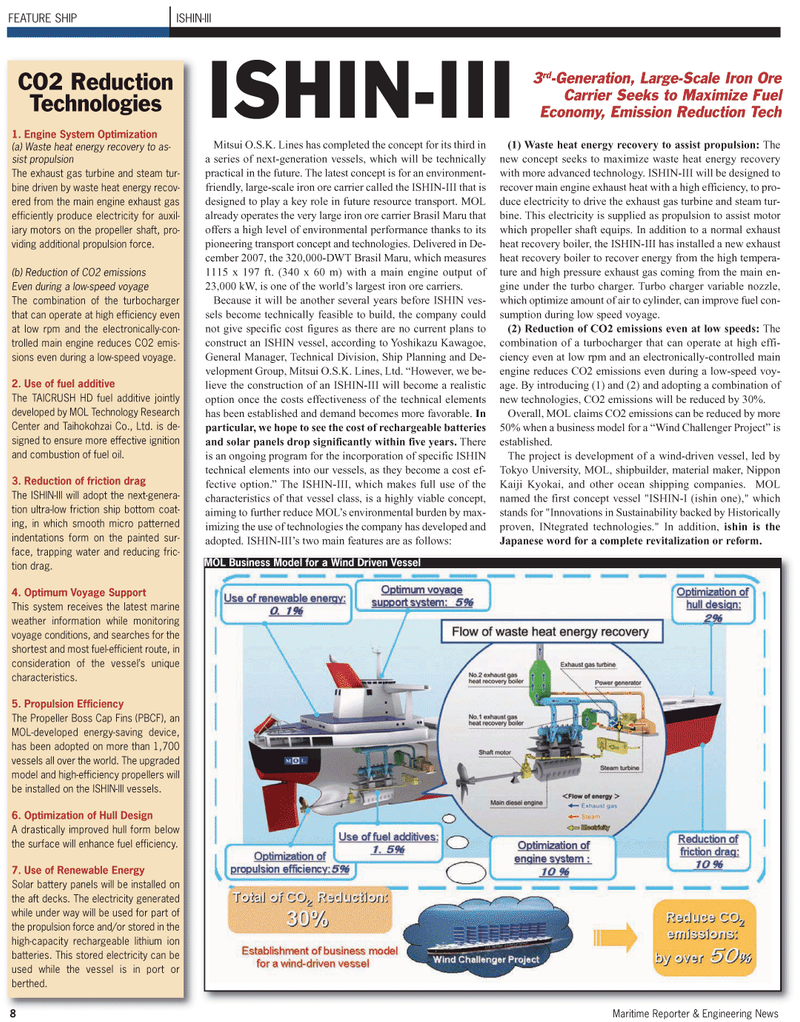
General Manager, Technical Division, Ship Planning and De- velopment Group, Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. “However, we be- lieve the construction of an ISHIN-III will become a realistic option once the costs effectiveness of the technical elements has been established and demand becomes more favorable. In particular, we hope to see the cost of rechargeable batteries and solar panels drop significantly within five years. There is an ongoing program for the incorporation of specific ISHIN technical elements into our vessels, as they become a cost ef- fective option.” The ISHIN-III, which makes full use of the characteristics of that vessel class, is a highly viable concept, aiming to further reduce MOL’s environmental burden by max- imizing the use of technologies the company has developed and adopted. ISHIN-III’s two main features are as follows: (1) Waste heat energy recovery to assist propulsion: The new concept seeks to maximize waste heat energy recovery with more advanced technology. ISHIN-III will be designed to recover main engine exhaust heat with a high efficiency, to pro- duce electricity to drive the exhaust gas turbine and steam tur- bine. This electricity is supplied as propulsion to assist motor which propeller shaft equips. In addition to a normal exhaust heat recovery boiler, the ISHIN-III has installed a new exhaust heat recovery boiler to recover energy from the high tempera- ture and high pressure exhaust gas coming from the main en- gine under the turbo charger. Turbo charger variable nozzle, which optimize amount of air to cylinder, can improve fuel con- sumption during low speed voyage. (2) Reduction of CO2 emissions even at low speeds: The combination of a turbocharger that can operate at high effi- ciency even at low rpm and an electronically-controlled main engine reduces CO2 emissions even during a low-speed voy- age. By introducing (1) and (2) and adopting a combination of new technologies, CO2 emissions will be reduced by 30%.
Overall, MOL claims CO2 emissions can be reduced by more 50% when a business model for a “Wind Challenger Project” is established.
The project is development of a wind-driven vessel, led by
Tokyo University, MOL, shipbuilder, material maker, Nippon
Kaiji Kyokai, and other ocean shipping companies. MOL named the first concept vessel "ISHIN-I (ishin one)," which stands for "Innovations in Sustainability backed by Historically proven, INtegrated technologies." In addition, ishin is the
Japanese word for a complete revitalization or reform.
ISHIN-III
CO2 Reduction
Technologies 1. Engine System Optimization (a) Waste heat energy recovery to as- sist propulsion
The exhaust gas turbine and steam tur- bine driven by waste heat energy recov- ered from the main engine exhaust gas efficiently produce electricity for auxil- iary motors on the propeller shaft, pro- viding additional propulsion force. (b) Reduction of CO2 emissions
Even during a low-speed voyage
The combination of the turbocharger that can operate at high efficiency even at low rpm and the electronically-con- trolled main engine reduces CO2 emis- sions even during a low-speed voyage. 2. Use of fuel additive
The TAICRUSH HD fuel additive jointly developed by MOL Technology Research
Center and Taihokohzai Co., Ltd. is de- signed to ensure more effective ignition and combustion of fuel oil. 3. Reduction of friction drag
The ISHIN-III will adopt the next-genera- tion ultra-low friction ship bottom coat- ing, in which smooth micro patterned indentations form on the painted sur- face, trapping water and reducing fric- tion drag. 4. Optimum Voyage Support
This system receives the latest marine weather information while monitoring voyage conditions, and searches for the shortest and most fuel-efficient route, in consideration of the vessel’s unique characteristics. 5. Propulsion Efficiency
The Propeller Boss Cap Fins (PBCF), an
MOL-developed energy-saving device, has been adopted on more than 1,700 vessels all over the world. The upgraded model and high-efficiency propellers will be installed on the ISHIN-III vessels. 6. Optimization of Hull Design
A drastically improved hull form below the surface will enhance fuel efficiency. 7. Use of Renewable Energy
Solar battery panels will be installed on the aft decks. The electricity generated while under way will be used for part of the propulsion force and/or stored in the high-capacity rechargeable lithium ion batteries. This stored electricity can be used while the vessel is in port or berthed. 8 Maritime Reporter & Engineering News 3 rd -Generation, Large-Scale Iron Ore
Carrier Seeks to Maximize Fuel
Economy, Emission Reduction Tech
MOL Business Model for a Wind Driven Vessel

 7
7
 9
9
