
Page 37: of Offshore Engineer Magazine (Jan/Feb 2015)
Read this page in Pdf, Flash or Html5 edition of Jan/Feb 2015 Offshore Engineer Magazine
Geology & Geophysics he Norwegian Petroleum relationship between density
Directorate (NPD) is currently and seismic velocity. The two
T offering acreage for license in the properties can be modeled formerly disputed zone of the Barents in most circumstances with
Sea, adjacent to the Norwegian-Russian a common structure, allow- border (Figure 1). ing the two datasets to be
The NPD has provided comprehen- interpreted cooperatively. sive 2D seismic coverage of the area to This gives the gravity mea- assist in the evaluation of the geology surement direct relevance and the nomination of the most interest- to the work of the seismic ing blocks. In addition, four 3D seismic interpreter.
surveys have recently been completed ARKeX deploys the within the area. Lockheed Martin Full Tensor
ARKeX has also recently completed Gravity Gradiometer, which a multi-client Full Tensor Gravity not only delivers the vertical
Gradiometry (FTG) survey covering the gravity gradient, but the hori- same area. zontal components (Gxx and
Industry interest in the area has
Gyy), as well as providing been very high, with over 30 compa- the full-tensor 3D measure-
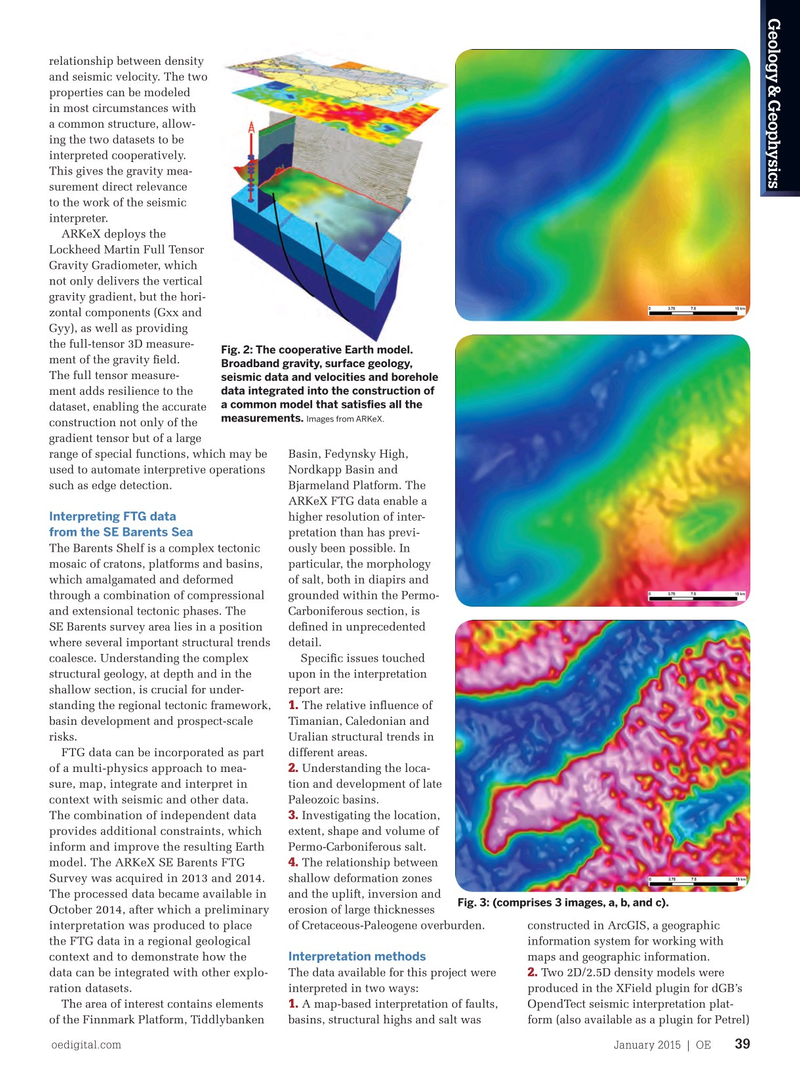
Fig. 2: The cooperative Earth model. nies reported to have subscribed to the ment of the gravity feld.
Broadband gravity, surface geology, 2D seismic database. The exploration
The full tensor measure- seismic data and velocities and borehole data integrated into the construction of potential of the Barents Sea in general ment adds resilience to the a common model that satisfes all the has been recognized for decades and a dataset, enabling the accurate measurements.
Images from ARKeX.
variable record of drilling success and construction not only of the failure is testament to the complex- gradient tensor but of a large ity and consequent exploration risk. range of special functions, which may be Basin, Fedynsky High,
However, the former disputed zone used to automate interpretive operations Nordkapp Basin and has, until recently, not seen the same such as edge detection. Bjarmeland Platform. The
ARKeX FTG data enable a level of academic and industry interest
Interpreting FTG data higher resolution of inter- given to the region as a whole, and is from the SE Barents Sea pretation than has previ- therefore still considered to be a new
The Barents Shelf is a complex tectonic ously been possible. In frontier.
FTG presents a relatively new way of mosaic of cratons, platforms and basins, particular, the morphology measuring the Earth’s gravitational feld which amalgamated and deformed of salt, both in diapirs and and mapping subsurface structures based through a combination of compressional grounded within the Permo- on varying density. Directly measuring and extensional tectonic phases. The Carboniferous section, is the gravity gradient in addition to the SE Barents survey area lies in a position defned in unprecedented usual measurement of acceleration due where several important structural trends detail.
to gravity results in vastly improved data coalesce. Understanding the complex Specifc issues touched resolution. structural geology, at depth and in the upon in the interpretation
Gravity gradients have long been shallow section, is crucial for under- report are: 1. used as a derivative of a conventional standing the regional tectonic framework, The relative infuence of measurement as a means of locat- basin development and prospect-scale Timanian, Caledonian and ing subsurface structure with greater risks. Uralian structural trends in
FTG data can be incorporated as part different areas.
precision. Measuring these quantities 2.
Understanding the loca- of a multi-physics approach to mea- directly adds confdence, enabling tion and development of late sure, map, integrate and interpret in familiar interpretational activities to
Paleozoic basins.
context with seismic and other data. be performed better while adding a 3.
Investigating the location,
The combination of independent data range of novel techniques to be devel- extent, shape and volume of provides additional constraints, which oped, which are compromised with
Permo-Carboniferous salt.
inform and improve the resulting Earth conventional gravimetry measurement. 4.
The relationship between
Integration of gravimetry and gradi- model. The ARKeX SE Barents FTG shallow deformation zones ometry measurements develops the
Survey was acquired in 2013 and 2014. and the uplift, inversion and capability to deliver “broadband grav-
The processed data became available in
Fig. 3: (comprises 3 images, a, b, and c).
erosion of large thicknesses ity measurement.” This is a valuable
October 2014, after which a preliminary of Cretaceous-Paleogene overburden. constructed in ArcGIS, a geographic dataset, capturing the long wavelength interpretation was produced to place information system for working with components of the feld that are driven the FTG data in a regional geological
Interpretation methods maps and geographic information.
by deep structure and the shorter wave- context and to demonstrate how the 2.
The data available for this project were Two 2D/2.5D density models were lengths that result from mid-crustal and data can be integrated with other explo- ration datasets.
interpreted in two ways: produced in the XField plugin for dGB’s near surface structure.
1.
Fundamental to the value of the broad- The area of interest contains elements A map-based interpretation of faults, OpendTect seismic interpretation plat- band gravity measurement is the close of the Finnmark Platform, Tiddlybanken basins, structural highs and salt was form (also available as a plugin for Petrel) oedigital.com January 2015 | OE 39 038_OE0115_G&G2_Arkex.indd 39 12/22/14 9:59 PM

 36
36
 38
38